Start date: 01-11-2021
End date: 09-06-2022
Clinical problem
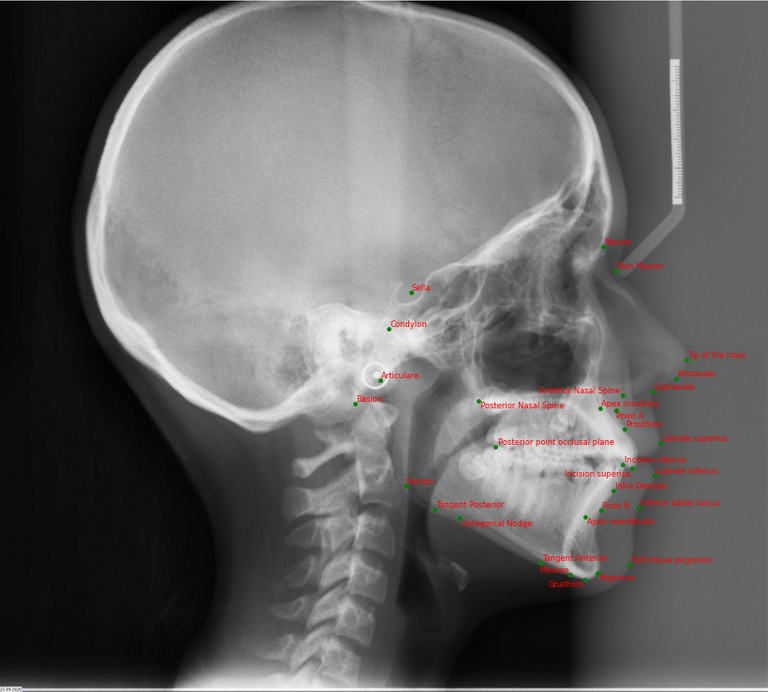
In Orthodontics, a lateral headplate (or cephalogram) is one of the diagnostic tools, used to compose an orthodontic diagnosis. On this lateral headplate a cephalometric analysis is performed to get an idea of facial growth, upper and lower jaw position and inclination, position and inclination of the teeth and soft-tissue position. This cephalometric analysis usually consists of at least 30 points and will result in different angles and distances, from which an orthodontic diagnosis can be made.
Today these cephalometric analyses are performed manually, which takes about 5 minutes per patient. In a normal orthodontic office, about 15-20 cephalometric analysis are performed per week. So, this costs the orthodontist 75-100 minutes every week. If this process can be automated by an AI model, this will save the orthodontist a lot of time.
Solution
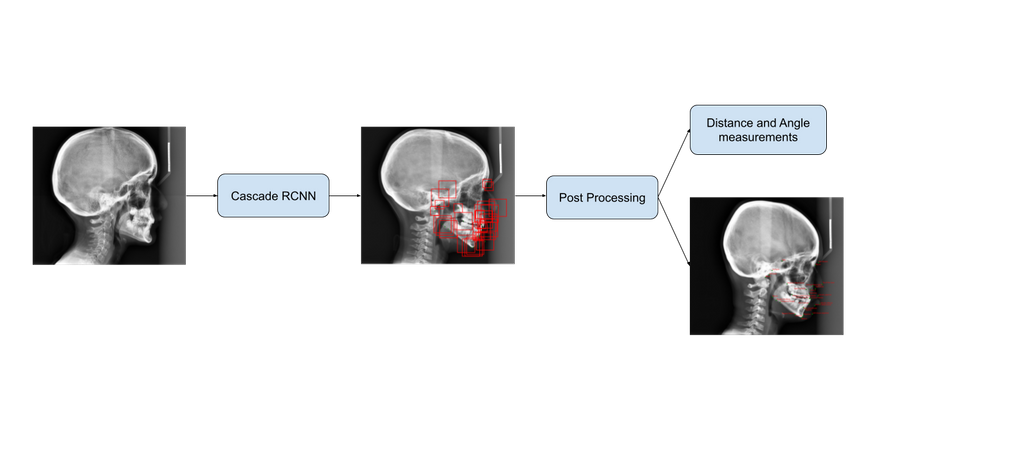
An object detection (OD) algorithm was built to find the anatomical landmarks by doing cephalometric analysis on lateral headplates. The algorithm predicts 31 bounding boxes from which landmark coordinates are extracted. Additionally, the algorithm also calculates clinically relevant angles and distance measurements using those landmark points. There are in total 8 distance and 16 angle measurements to be calculated after the cephalometric analysis.
The algorithm predicts accurate annotations and the average inference time for the model is 13 seconds. The model results should be supervised by an expert orthodontist. The algorithms output can be visualised on the CIRRUS platform. The angle and distance measurements are stored in a PDF file and can be downloaded from the CIRRUS platform.
Below you can see the architecture of the network.
Data
The data consists of 1000 lateral headplates (x-rays), made at the department of Dentistry - Orthodontics and Craniofacial Biology. The landmarks will be determined by 2 trained experts, in the grand challenge platform. In the pre-processing stage the annotations are converted into COCO dataset format to train the OD network. In total 31 landmark annotations are present for each scan.
Results
The object detection network achieved a Mean Radial Error (MRE) of 1.14 with a Standard Deviation (SD) of 0.82. The network had an average precision of 0.857 for IoU = 0.50:0.95 with a step size increase of 0.05 in the IoU. The Success Detection Rate (SDR) of the network for 2mm error threshold was 85.62%. The Detection Accuracy (DA) of the network was 99.84%. This is the only drawback of the network. Since, an orthodontist can always place all the 31 points on the image, whereas the network might fail to do some in some rare cases.
Conclusion
An object detection network was built to automate the cephalometric analysis process. The network predicts 31 landmark points and calculates 8 distance and 16 angle measures. The model can be improved by training on data from different machines and annotations from more orthodontist. This will help model generalize better and produce robust results. A future work can involve the addition of a heatmap regressor network on the output of the object detection model.
An interactive demo is accessible via Grand-Challenge: Try out the algorithm
The code for this project can be found in this GitHub repository. The detailed report about the algorithm and the results can be viewed here


