Background
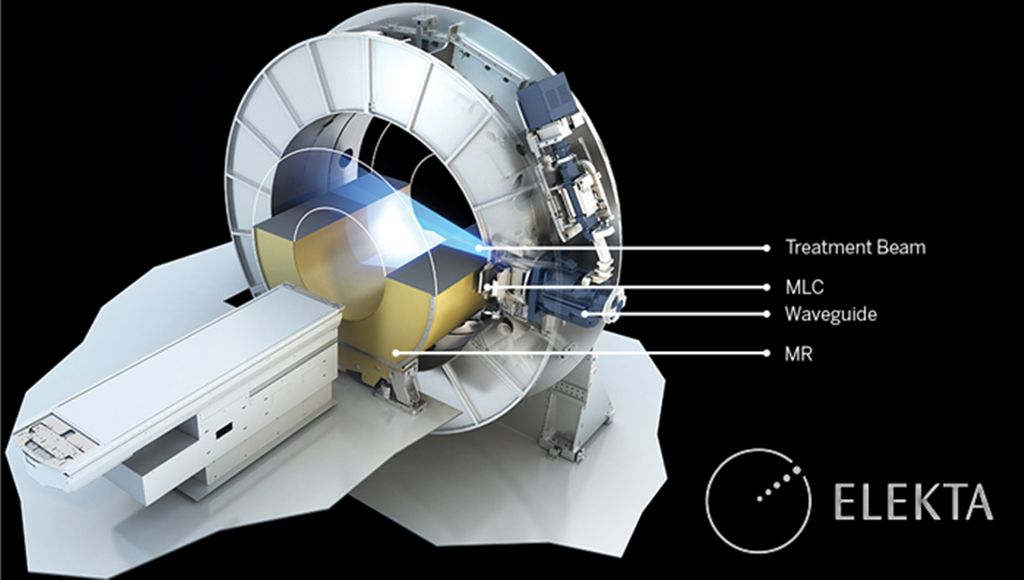
In radiation therapy a device called the linac shoots beams of high energy photons at a tumor, killing its cells. Unfortunately, this can damage nearby healthy tissue as well so we have to aim very carefully, which is difficult when tumors are located in organs that move a lot (breathing, heartbeat, etc). But there is a solution: The Radboudumc is one of a few places in the world that house an MR-Linac, a linac built inside an MRI scanner. Using MRI we can rapidly make images of the moving tumor and its surroundings and adjust the photon beam accordingly. This is where you come in...
We are looking for a PhD student to develop Artificial Intelligence tools to automatically detect healthy organs and tumors in the MR images. At present this is done manually at the start of a treatment session. This takes such a long time that it prevents effective (real-time) beam adaptation. Your role will be to create deep-learning networks that can delineate the relevant structures in the image in a flash. Secondly, you will create MRI protocols that allow faster scanning and with improved tissue/tumor contrasts to facilitate aforementioned delineation and also treatment efficacy evaluation. You will closely work together with a second PhD student on this project, who will develop tools that use the delineation results to steer the linac’s beams more efficiently and effectively. Ultimately, the goal is to accelerate the entire workflow to such an extent that real-time beam adjustments can be achieved.
Profile
You are a creative and ambitious researcher with an MSc degree in Biomedical engineering, Computer science, A.I., Medical imaging, Physics or similar, with a clear interest in artificial intelligence and medical image analysis. Good communication and organizational skills are essential. Experience with deep learning and programming, preferably in Python, are a plus.
Organization
Radiation Oncology department
Our group operates at the interface of the Radiation Oncology department and the Diagnostic Image Analysis Group (DIAG) which is housed in the Radiology department. The Radiation Oncology department is a clinical department where patients are treated using a variety of radiotherapy devices including the MR-Linac, and where research takes place varying from investigations on the molecular structure of tumor and immune cells to the improving the daily treatment routine. Due to the very technologically advanced nature of the treatment modality, the department has a very large clinical physics team to both develop methods for, and maintain the high-tech radiation therapy devices.
Diagnostic Image Analysis Group (DIAG)
The DIAG is a very large research group heavily focused on developing AI methods for medical image analysis over a wide range of imaging modalities. It runs the world-leading medical AI challenges platform which brings together AI researchers, medical specialists and medical technology industry.
Radboudumc
Radboud university medical center is a university medical center for patient care, scientific research, and education in Nijmegen. Radboud university medical center strives to be at the forefront of shaping the healthcare of the future. We do this in a person-centered and innovative way, and in close collaboration with our network. We want to have a significant impact on healthcare. We want to improve with each passing day, continuously working towards better healthcare, research, and education. And gaining a better understanding of how diseases arise and how we can prevent, treat, and cure them, day in and day out. This way, every patient always receives the best healthcare, now and in the future. Because that is why we do what we do.
Read more about our strategy and what working at Radboud university medical center means. Our colleagues would be happy to tell you about it. #weareradboudumc
Application
Please apply before Aug 22nd, 2022 via this link. Here you can also find more information on the application process and what needs to be included in your application.

