Background
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide, for which the five-year survival rates have yet to surpass 20%. Tobacco smoking remains the main risk factor for lung cancer. Although there is a decreasing prevalence of smokers in most countries, tobacco control is not the only measure for decreasing lung cancer mortality. In 2011, the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) was the first multicenter randomized controlled trial (RCT) to demonstrate that three rounds of annual screening of a high-risk population using low-dose chest computed tomography (CT) lead to 20% fewer lung cancer deaths after seven years of follow-up, compared to annual screening with chest radiography. Over 53,000 participants were included in this landmark study. The Dutch-Belgian NELSON trial – the second largest RCT with 15,789 participants – recently published their results and showed a 24% mortality reduction in a high-risk population of men compared to no screening.
Problem description
If a population were invited for screening based on age and long-term smoking behaviour (like in NELSON), many individuals would not benefit. Many screenees have a low risk of lung cancer despite their smoking history (in NELSON <4% developed lung cancer), while some screenees have insufficient life expectancy to benefit from screening. Secondly, screen-detected lung nodules lead to extra investigations in 25-30% of screenees while most are benign. Thus, there is a critical need for stricter selection of screenees who will benefit from screening, and for improved nodule stratification.
Research direction
We offer a fully-funded PhD position that focuses on improving the efficiency of lung cancer screening by using artificial intelligence (AI). This position is a PhD position within a larger consortium project: NELSON-POP. In this consortium, the unique expertise and data from the various NELSON sites and associated research groups are combined to leverage various unexplored data sources, in order to identify the factors most predictive of lung cancer. Using multi-source data, the consortium aims to maximize lung cancer screening efficiency, by developing prediction models to 1) optimize screenee selection, and 2) limit unnecessary nodule work-up.
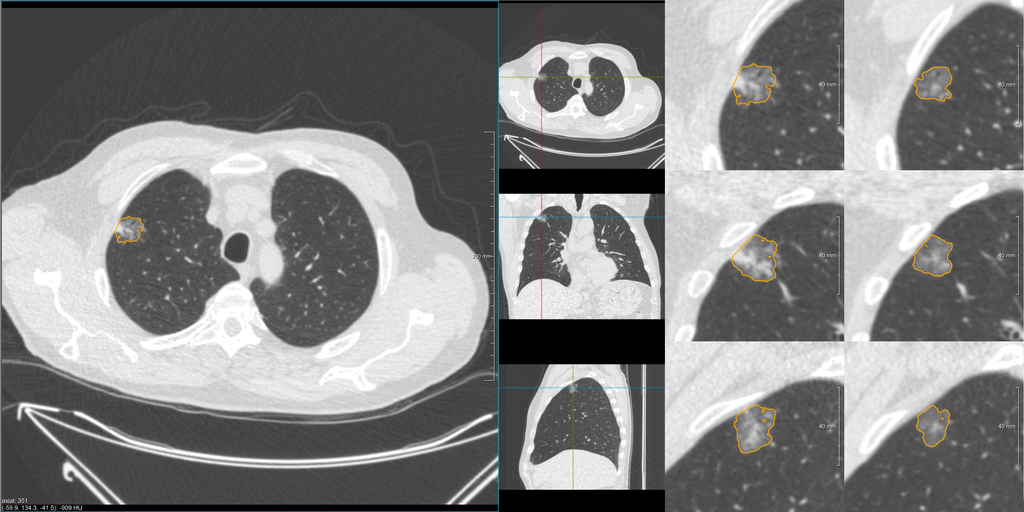
This PhD position focuses on the use of existing AI algorithms for lung cancer screening. AI algorithms based on deep learning have great potential to perform more reproducible and more objective pattern recognition and thereby may increase the accuracy and consistency of malignancy probability estimation of pulmonary nodules. This increased accuracy can be used to develop optimized follow-up protocols, leading to less unnecessary follow-up CTs and unnecessary referrals in lung cancer screening. Therefore, the aim of this PhD project is to accurately determine the probability of lung cancer of screen-detected pulmonary nodules using artificial intelligence in order to reduce the number of unnecessary repeat scans and unnecessary referrals, all contributing to reduction of radiation exposure, financial expenses, workload, invasive procedures, and screenee anxiety.
You will use existing AI algorithms developed and validated by the Radboudumc group. You will validate the accuracy of the AI algorithms on the NELSON cohort and investigate how these can be used to develop novel optimized nodule management guidelines. You will work in close collaboration with a team of technical PhD candidates, research software engineers, and radiologists. Your daily supervision will be performed by Colin Jacobs. Your PhD supervision team will also involve supervisors from the other NELSON sites, to contribute to the synergy necessary to reach the goals of the consortium.
The research should result in a Ph.D. thesis.
Requirements
For this project at the department of Medical Imaging at Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen (The Netherlands), we are seeking an enthusiastic PhD student with a clear interest in the potential that AI techniques may have in the field of radiology. This is an excellent opportunity to assess the value of this cutting-edge technology and investigate its potential to more personalized lung cancer screening.
Tasks and responsibilities
Within this project you will:
- Validate the predictive power of AI algorithms on the NELSON cohort.
- Compare the AI algorithms with a panel of expert radiologists and existing risk models for estimating lung cancer risk.
- Determine an optimized nodule management algorithm by including the AI risk score.
- Investigate how AI biomarkers can contribute to the final predictive model of the consortium, which also includes environmental factors, polygenic risk scores, and biomarkers for COPD, coronary artery disease and emphysema to estimate the personalized risk of lung cancer.
Profile
You should be a creative and enthusiastic researcher with a MSc in a relevant field, such as medicine, technical medicine, clinical epidemiology, or similar. Interest in medical imaging, with a particular focus on oncologic (lung) imaging and artificial intelligence. Interest in and preferably experience with scientific research.
Organisation
The Diagnostic Image Analysis Group is a research group of the Department of Medical Imaging of the Radboud University Medical Center. We develop, validate and deploy novel AI algorithms in healthcare. This PhD position falls with the lung cancer image analysis research line led by Colin Jacobs. We actively collaborate with many international players in the field of lung cancer screening, and have a strong focus on integration of our AI algorithms into clinical practice.
Terms of employment
Starting date is preferably Dec 1, 2021. The project will appoint a PhD candidate for 4 years in total. Your performance will be evaluated after 1 year. If the evaluation is positive, the contract will be extended by another 3 years. The gross monthly salary, depending on education will be scale 10A or scale 10 based on a full-time working week (excl. vacation bonus and 8,3% end of year payments). Upon commencement of employment we require a certificate of conduct (Verklaring Omtrent het Gedrag, VOG) and there will be, depending on the type of job, a screening based on the provided cv. Radboud university medical center’s HR Department will apply for this certificate on your behalf. Read more about the Radboudumc employment conditions and what our International Office can do for you when moving to the Netherlands.
Application
Applications will be reviewed on an ongoing basis until the position is filled. For more information about the vacancy, please contact Colin Jacobs. Use this link to apply.


